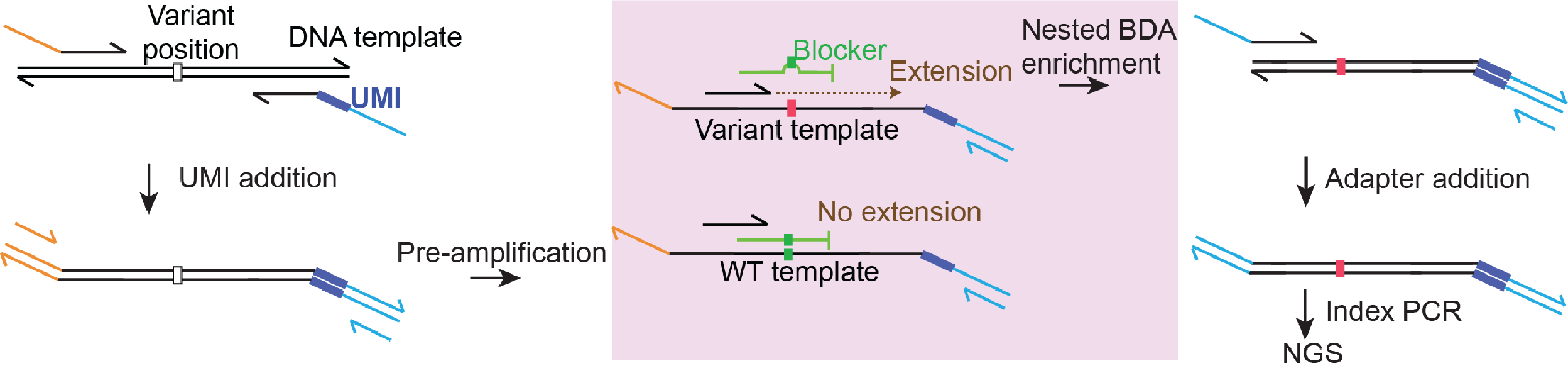
Overview
There are millions of DNA sequences in a patient’s sample. Rare variant sequences contain vital disease-state information, but current technologies struggle to detect these rare variant sequences.
Our proprietary methodology, blocker displacement amplification (BDA) is a PCR-based rare allele enrichment method that allows for accurate detection and quantitation of SNVs and indels down to 0.01% VAF in a highly multiplexed environment. BDA improves the limit of detection on NGS and PCR platforms.